SaaS Deployment Model
-
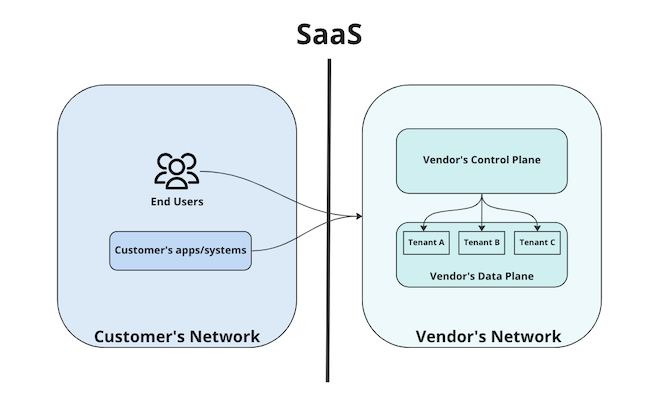
The vendor’s “Data Plane” (where the apps and software for each customer are hosted and running) is in the vendor’s network.
-
The infrastructure — machines, memory, CPU, disk — is, therefore, provided by the vendor
What is Private SaaS?
-
Private SaaS is a cloud-based software delivery model that provides all the benefits of traditional SaaS, with one key difference: the software runs on a private or dedicated cloud infrastructure rather than a shared public one.
-
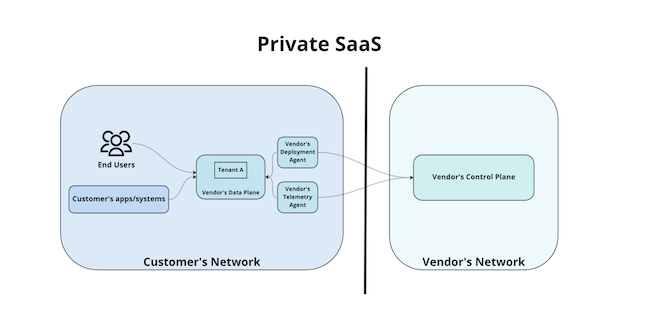
So Private SaaS is a variation of SaaS where the provider runs the software within the customer’s network but takes the responsibility for managing and securing it.
-
The vendor’s “Data Plane” lives in an environment within Customer A’s network and is therefore managed and controlled by Customer A.
-
The infrastructure — machines, memory, CPU, disk — is provided by Customer A.
-
Only the vendor’s “Control Plane” (which is responsible for what updates go out to the “Data Plane”) lives within the vendor’s infrastructure, while the tools and apps reside in the customer’s infrastructure.
What are the differences between SaaS, Self-Hosting and Private SaaS?
| Feature | SaaS | Self-Hosted | Private SaaS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Managed by | Provider | Self | Provider |
| Reliability | High | Low | High |
| Security hardening | High | Low | High |
| Operational overhead | Low | High | Medium |
| Time to value | Quick | Slow | Quick |
| Data residency | Not Available | Full Control | Full Control |
| Data governance | Not Available | Full Control | Full Control |
| Compliance | High dependency on the provider | No external dependency | Some dependency on the provider |
| Data transfer costs | High | Low | Low |
